"Why has this not been taught in schools?" - Maharshi Sushruta, the first surgeon.
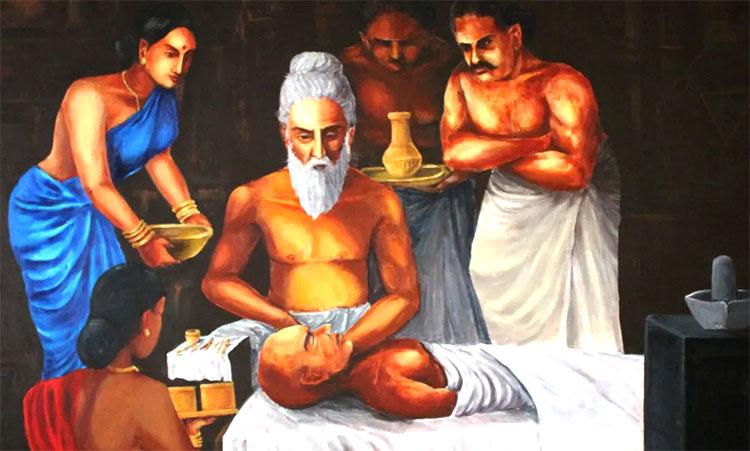

Maharshi Sushruta was a renowned ancient Indian physician and surgeon who is widely considered as the father of modern surgery. He lived around 600 BCE, during the Vedic period of ancient India, and authored the Sushruta Samhita, an important treatise on Ayurvedic medicine and surgery.
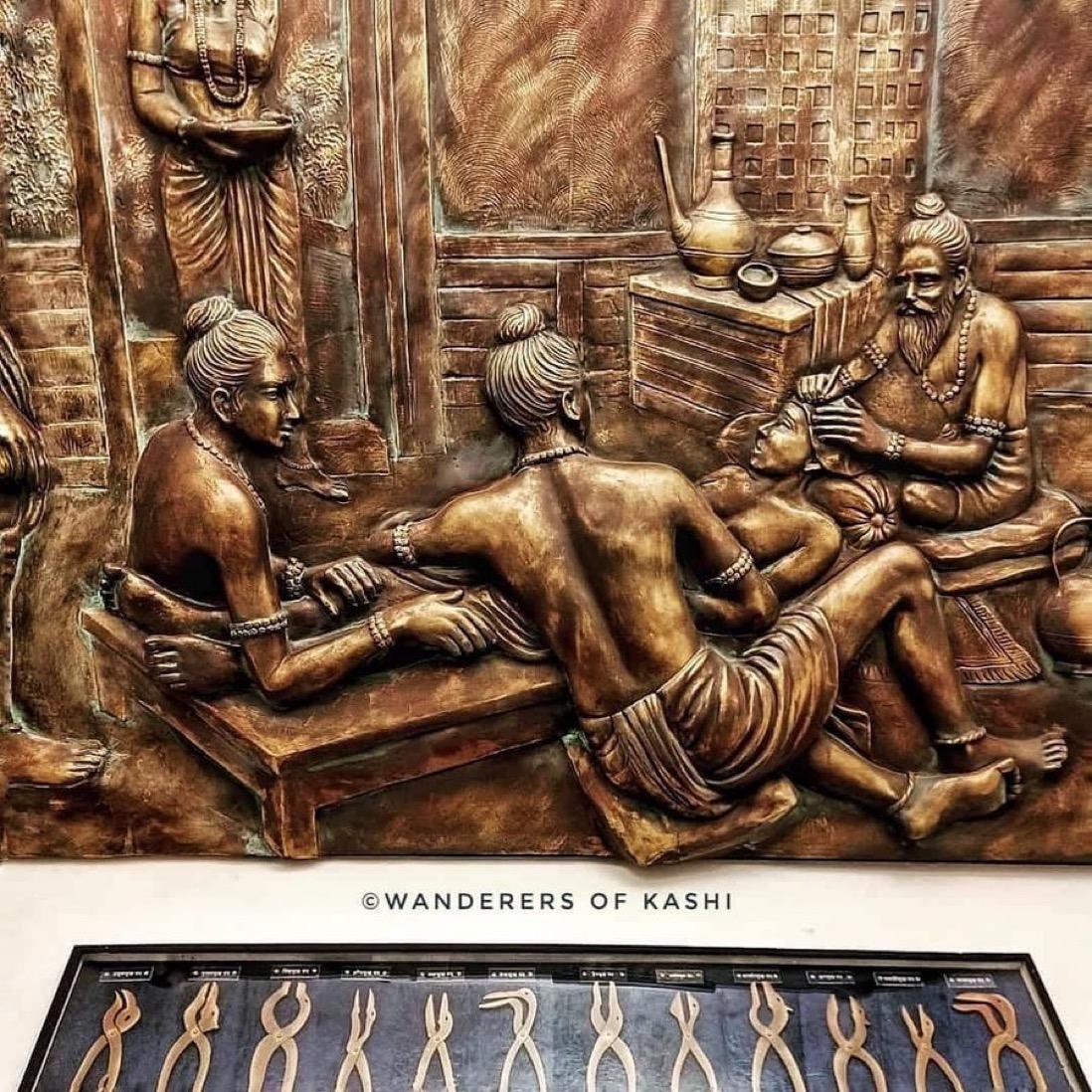

Sushruta was born in the city of Kashi (present-day Varanasi) in northern India, and received his education in Ayurveda and surgery from his father, Vishvamitra, who was also a physician. He later traveled to Taxila (present-day Pakistan) to study under renowned scholars of the time.

Sushruta's contributions to the field of medicine and surgery were significant. He developed several surgical techniques, including the use of surgical instruments such as scalpels, forceps, and scissors. He also described various surgical procedures, such as rhinoplasty (nose surgery) and cataract surgery.
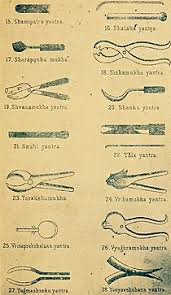
One of Sushruta's most notable achievements was the development of the technique of pedicle flap surgery, which involves taking tissue from one part of the body and using it to repair a defect or injury in another part of the body. This technique is still used today in modern surgical procedures.
Sushruta also contributed to the field of Ayurvedic medicine, and his Sushruta Samhita remains an important text in Ayurveda to this day. The treatise is divided into six sections, and covers a wide range of topics related to medicine and surgery, including anatomy, physiology, pathology, and pharmacology.

- Political Leaders
- Art & Crafts
- Dance & Music
- Sanatan Dharma
- Education & Training
- Food & Drinks
- Gaming
- Health & Fitness
- Home & Gardening
- Literature & Culture
- Love
- Medicine & Ayurveda
- Motors & Vehicles
- Movies & Cinema
- Parenting
- Politics
- Science & Technology
- Shopping
- Social Media
- Spirituality
- Sports
- War & History
- Yoga & Meditation
- Travel & Tourism
- Natural Disaster
- Business & Startups
- DIY & Home Decor
- Finance
- Personal
- News
- Pet Lovers
- Wild Life & Nature
- Podcast & Audio Books
- Poetry
- Law & Order
- Moral Stories
- Jokes & Humour
- Other

